Colour Schemes
Cyclone Manual - Colour Schemes
Throughout the 2D and 3D views, colour schemes are required when working with contours. Cyclone provides a large library of built-in colour schemes, and users can either create new schemes based on these or define entirely new schemes manually.
Multiple Colour Schemes Example
JSON1{ 2 "colour schemes": [ 3 { 4 "name": "Greyscale", 5 "Values": [0, 1], 6 "Colours": [ 7 [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0], 8 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 9 ] 10 }, 11 { 12 "name": "HotMetal", 13 "Values": [0, 2, 5, 10], 14 "Colours": [ 15 [0.2, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0], 16 [1.0, 0.4, 0.0, 1.0], 17 [1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0], 18 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 19 ] 20 } 21 ] 22}
Required Fields
Each colour scheme entry must include:
-
Name – Unique identifier for the colour scheme.
-
Values – Array of numeric breakpoints (must be increasing).
-
Colours – Array of RGBA values corresponding to each breakpoint.
-
Each colour must be an array of four floats: [R, G, B, A].
-
R, G, B, A must all be normalised between 0.0 and 1.0.
-
The number of colour entries must match the number of values.
Import Process
-
Open the Colour Scheme Database.
-
Click the Import Colour Scheme button (bottom-right).
-
Select a JSON file.
-
The file will be validated:
-
Every entry must have a name.
-
Both Values and Colours must be provided.
-
Length of Values and Colours arrays must match.
-
Successfully imported colour schemes are stored in local storage under "colour-schemes".
After Import
-
Imported schemes appear in the colour scheme database.
-
They can be used immediately for gradient mapping in the visualiser.
-
They can also be exported again in JSON format.
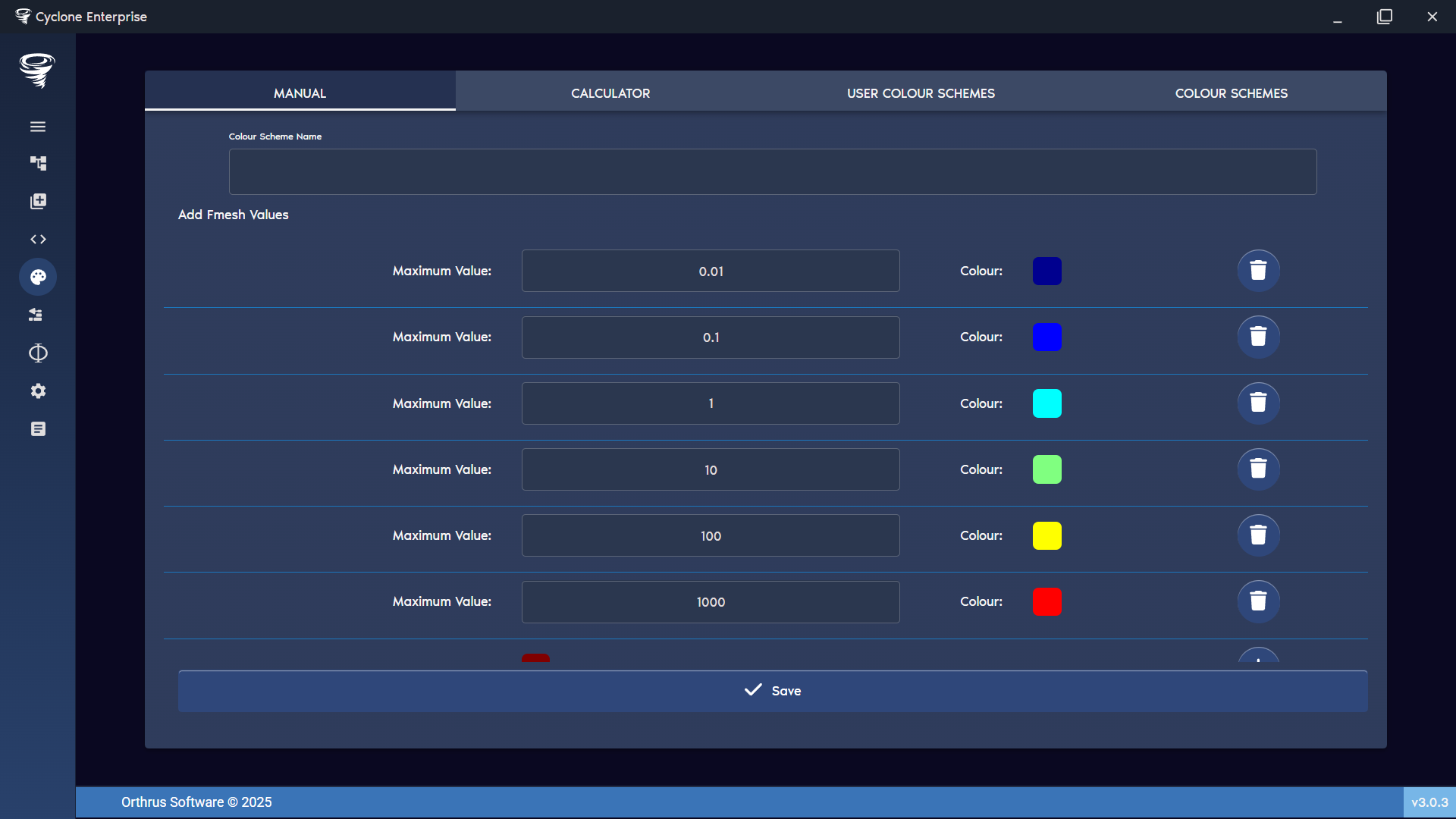
Figure 90: colour creator – manual
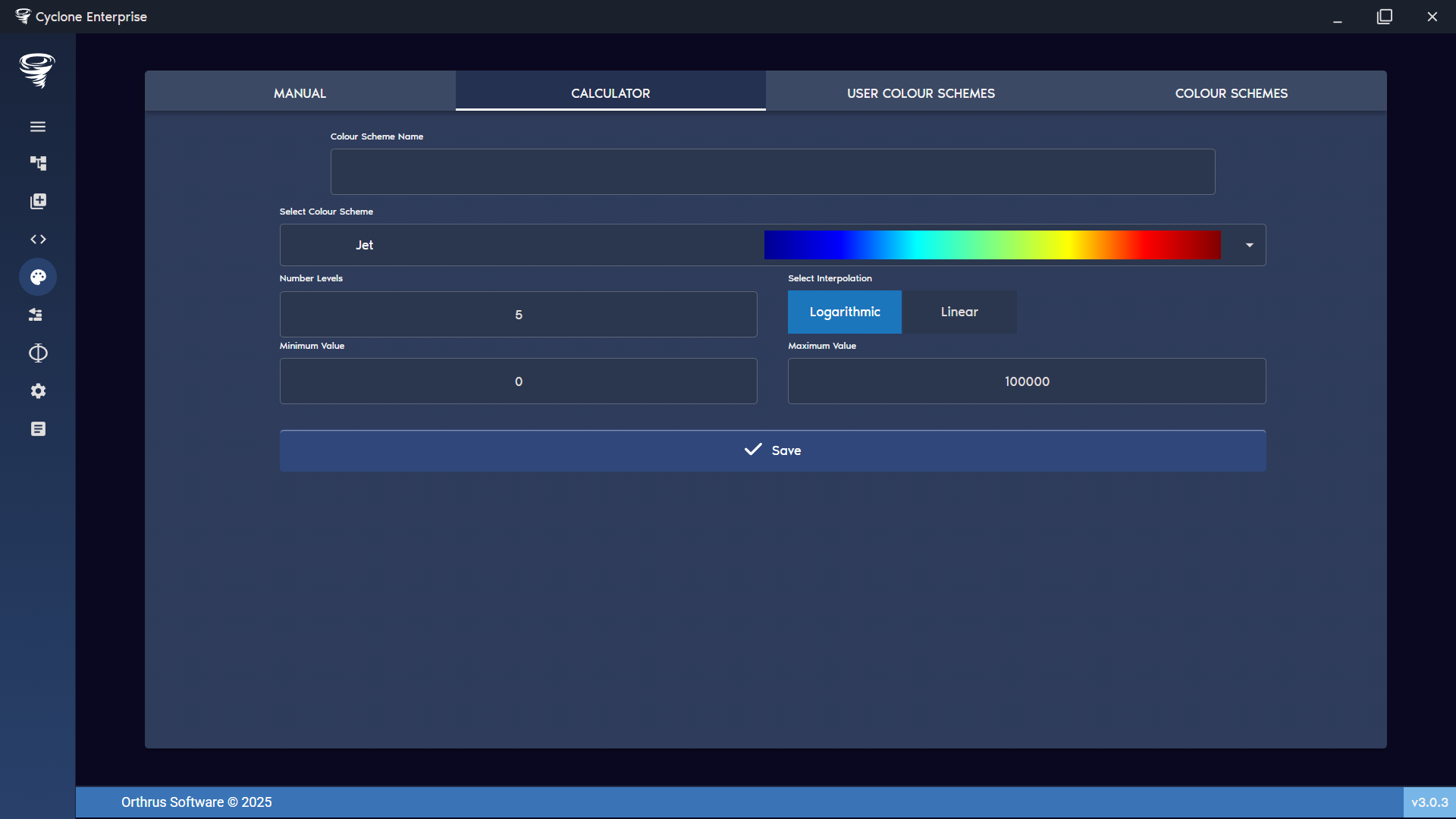
Figure 91: Colour creator – calculator
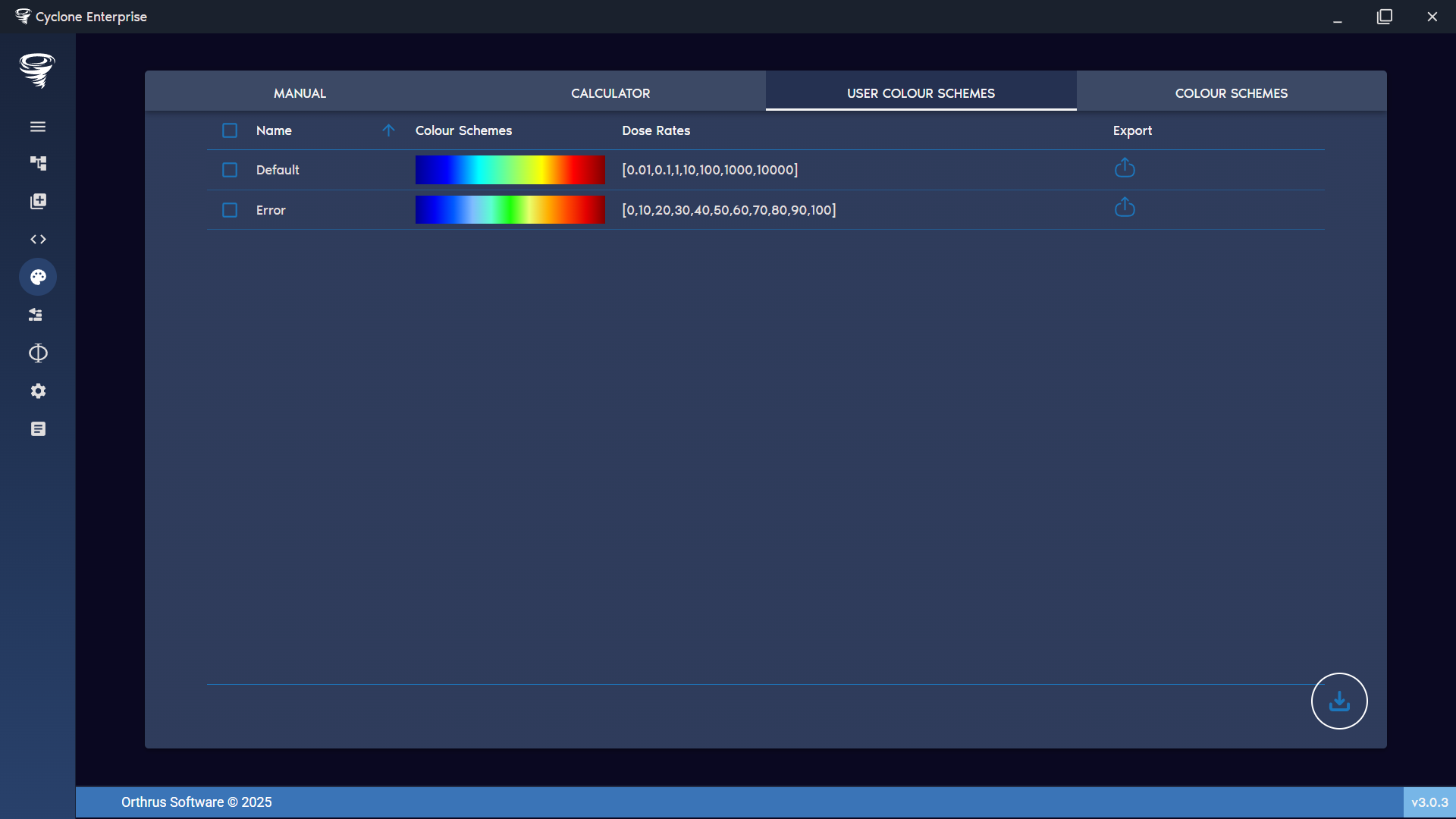
Figure 92: Colour creator – user colour schemes
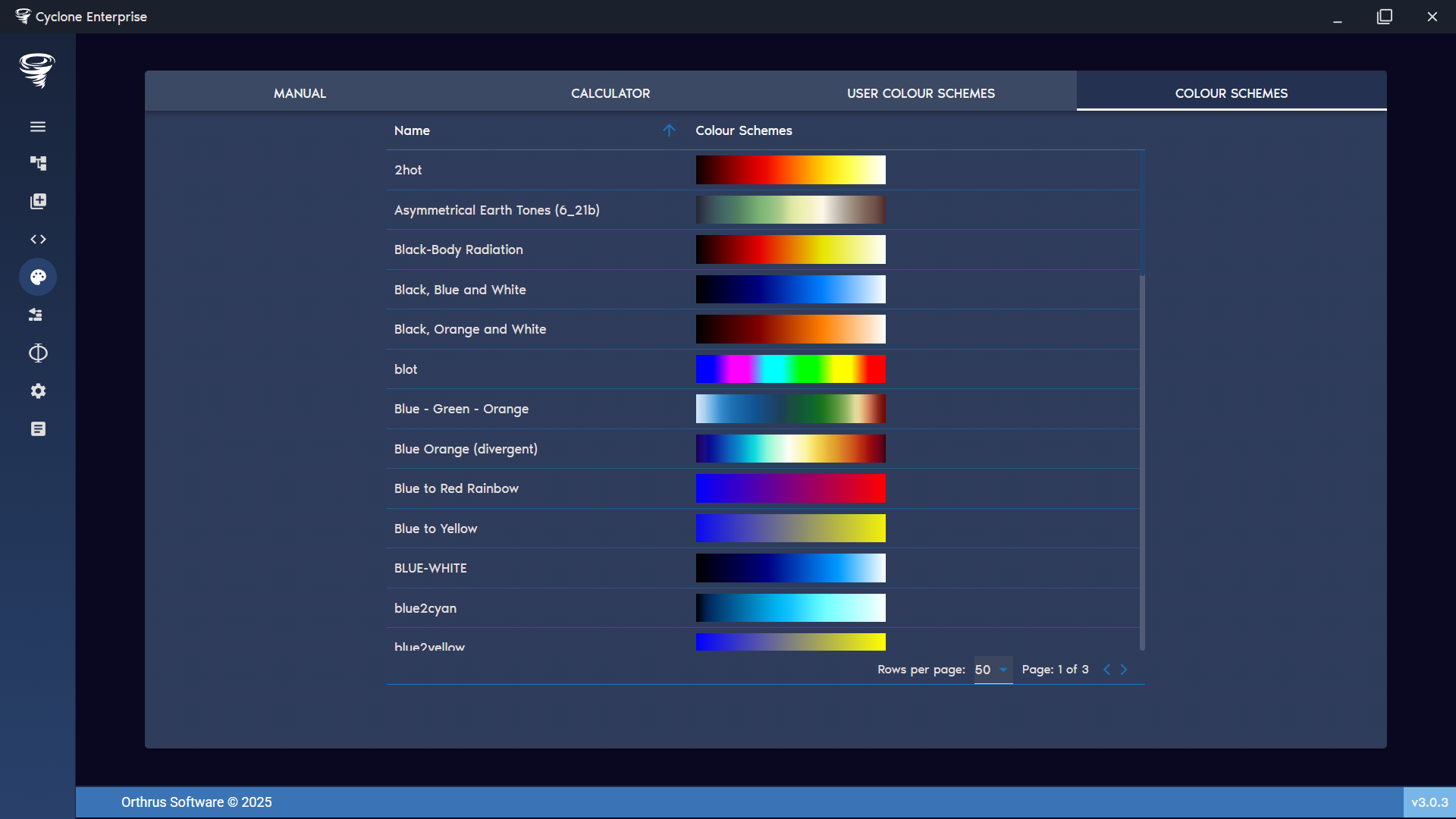
Figure 93: Colour creator – in-built colour schemes