Materials
Cyclone Manual - Materials
Materials can be inserted directly into an MCNP input through the Code Editor. New materials may be defined in several ways:
-
Mixing existing materials.
-
Creating a material from scratch.
-
Importing or exporting materials for reuse.
Material Calculator
A new material can be created by mixing one or more existing materials (Figure 94). When defining the mixture, the user can specify the material format and fraction type. In addition, default nuclear cross-section libraries and thermal neutron scattering cards can be attached to the material. All default options can be overridden at the point of insertion.
Mixing is currently restricted to the materials defined in [5], although, future development will expand this functionality to support calculations for fully user-created materials.
Manual Material Creator
In addition to the material calculator, manual materials can be created by selecting isotopes and defining their weight or atom fractions (Figure 95). Default values (such as cross-section libraries or thermal scattering data) can also be attached to the material. As with other material types, these defaults may be overridden at the point of insertion.
Single Material Example
JSON1{ 2 "Name": "Stainless Steel", 3 "Density": 7.8, 4 "Fraction Type": "atom fraction", 5 "Format": "isotopic", 6 "zaids": [ 7 { "zaid": "26000", "fraction": 0.70 }, 8 { "zaid": "28000", "fraction": 0.18 }, 9 { "zaid": "24000", "fraction": 0.12 } 10 ], 11 "Thermal Cards": [ "lwtr" ], 12 "NLIB": "ENDF70SaB", 13 "PLIB": "ENDF70SaP", 14 "GAS": 0, 15 "ESTEP": 2, 16 "HSTEP": 1, 17 "COND": 0, 18 "REFI": "", 19 "REFS": "" 20}
Multiple Materials Example
JSON1{ 2 "materials": 3 { 4 "Name": "Graphite", 5 "Density": 1.7, 6 "Fraction Type": "atom fraction", 7 "Format": "isotopic", 8 "zaids": [ 9 { "zaid": "6000", "fraction": 1.0 } 10 11 }, 12 { 13 "Name": "Aluminium", 14 "Density": 2.7, 15 "Fraction Type": "weight fraction", 16 "Format": "isotopic", 17 "zaids": 18 { "zaid": "13027", "fraction": 1.0 } 19 20 } 21 ] 22}
Required Fields
At minimum, a material JSON must include:
-
Name – Unique material identifier.
-
Density – Material density (float).
-
Fraction Type – Either "atom fraction" or "weight fraction".
-
zaids – Array of isotopes and their fractions. Each entry must include:
-
"zaid" – Isotope identifier.
-
"fraction" – Fraction of the isotope.
Optional Fields
-
Format – Defaults to "isotopic" if omitted.
-
Thermal Cards – List of thermal neutron scattering treatments.
-
Cross Section Libraries – Any of the following (maps to MCNP card names):
-
NLIB, PLIB, PNLIB, ELIB, HLIB, ALIB, TLIB, DLIB
-
Other Data:
-
GAS – Gas density-effect correction.
-
ESTEP – Electron sub-steps.
-
HSTEP – Charged particle sub-steps.
-
COND – Conduction state.
-
REFI – Constant refractive index.
-
REFS – Cauchy coefficients.
Import Process
-
Open the Material Database Table.
-
Click the Import Material button (bottom right).
-
Select the JSON file.
-
The file will be validated:
-
All isotopes (zaids) must have matching fractions.
-
A density and fraction type must be provided.
-
If fields are missing, the user will be notified with an error.
-
Successfully imported materials are stored in local storage under "custom-materials".
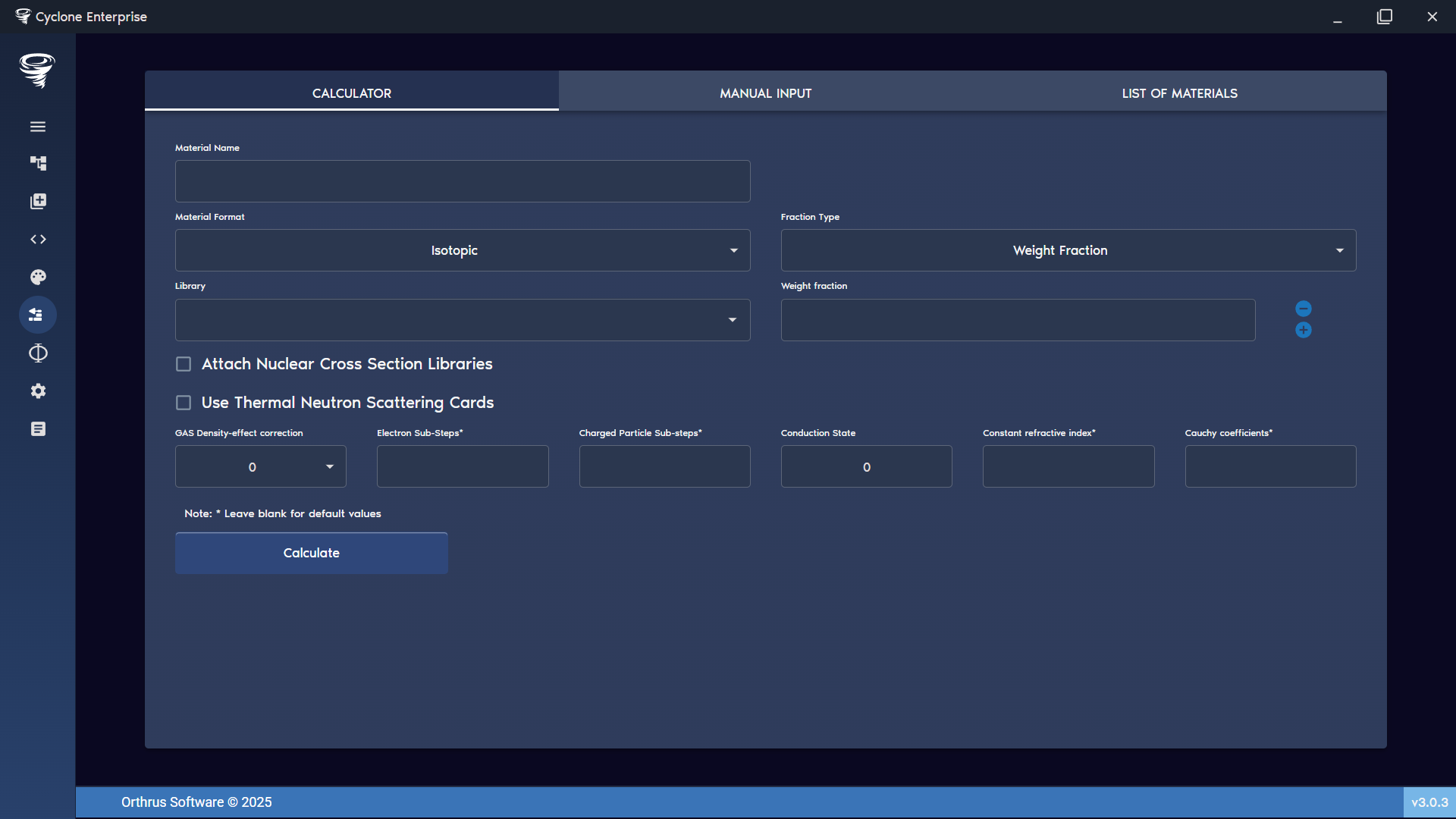
Figure 94: Material creator – calculator
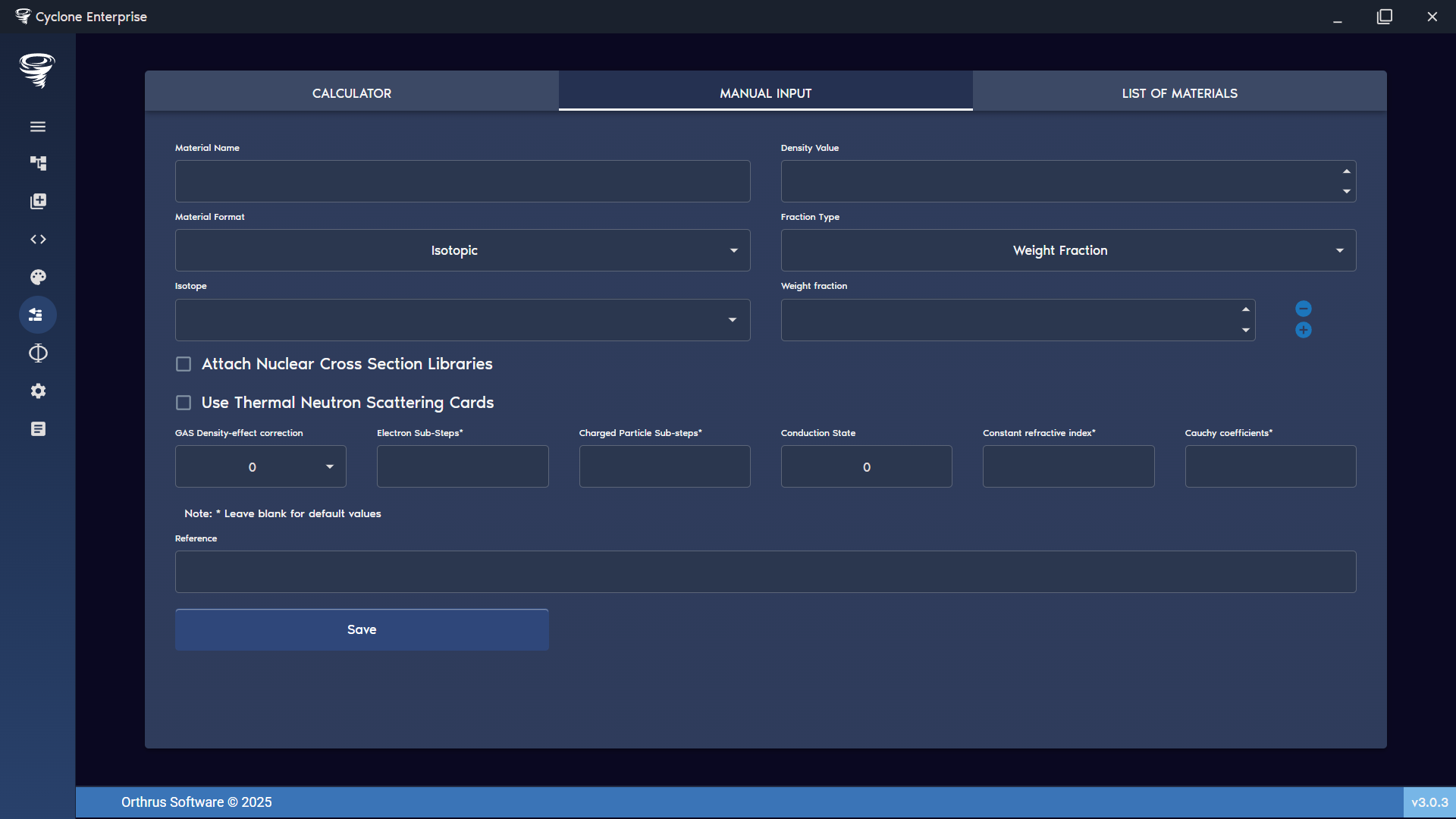
Figure 95: Material creator – manual input
Figure 96: Material creator – user materials